Introduction
Limb lengthening procedures have come a long way in helping individuals achieve their desired proportions and overcome physical limitations. One of the innovative techniques gaining attention is “bone transport.” This advanced method allows for gradual limb lengthening while maintaining structural integrity, offering new hope for those seeking improved aesthetics and function.
Understanding Bone Transport
What is Bone Transport?
Bone transport is a surgical technique employed in limb lengthening procedures. Unlike traditional methods that involve single-site bone fractures, bone transport involves gradually moving a segment of bone to achieve lengthening while preserving blood supply and bone quality.
How does Bone Transport Work?
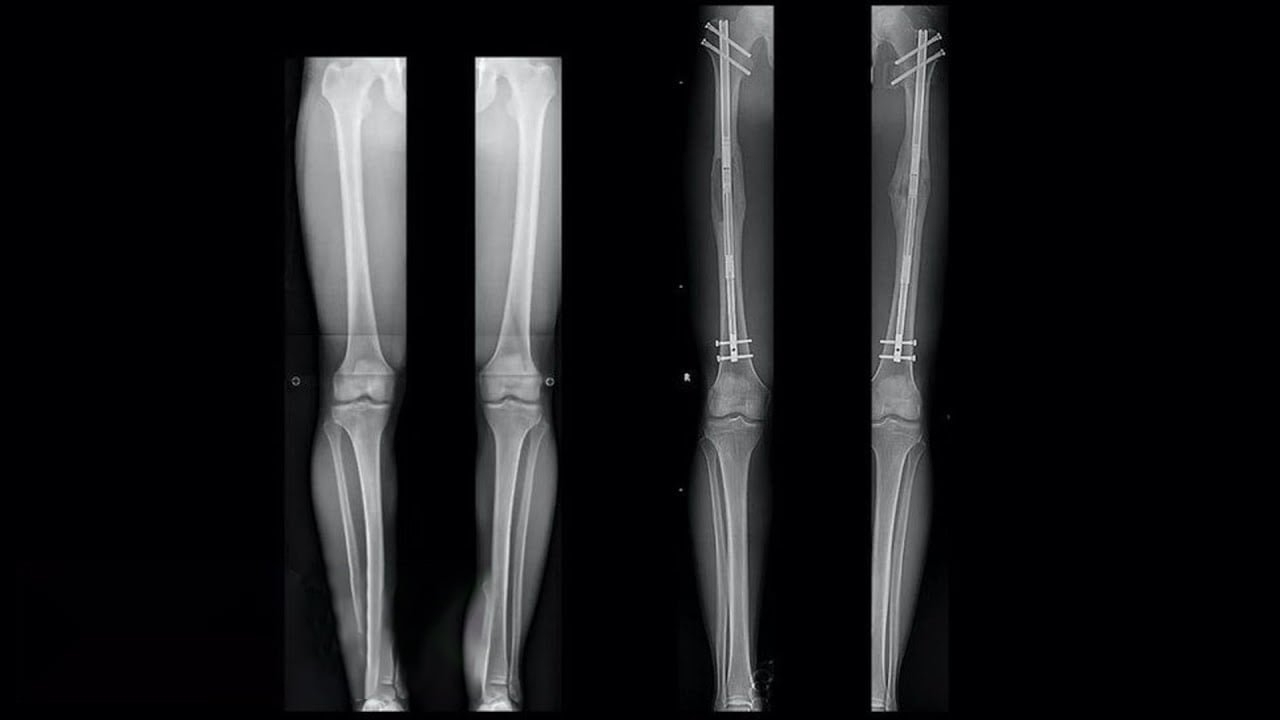
The procedure begins with the placement of external fixators on either side of the bone segment to be lengthened. These fixators provide stability and control during the lengthening process. Through controlled distraction, the bone segment is gradually moved, allowing new bone to form in the gap.
Applications of Bone Transport
Bone transport is not limited to cosmetic lengthening. It is also utilized to address congenital limb length discrepancies, post-traumatic deformities, and cases requiring bone defect reconstruction.
The Procedure: Step-by-Step
Preoperative Assessment
Before surgery, a comprehensive evaluation is conducted to determine the patient’s suitability for bone transport. X-rays, CT scans, and medical history play a crucial role in planning.
Surgical Placement of External Fixators
During surgery, external fixators are surgically attached to the bone above and below the target segment. These fixators serve as anchoring points for the gradual lengthening process.
Initiating Bone Transport
Following the surgery, controlled distraction of the bone segment begins. The fixators are adjusted at specific intervals, allowing the bone to move gradually without compromising its integrity.
Monitoring Progress
Regular follow-up appointments and imaging help monitor the progress of bone formation and alignment. Adjustments to the fixators are made based on the healing process.
Removal of Fixators
Once the desired length is achieved and the bone segment has healed adequately, the external fixators are removed. Physical therapy and rehabilitation play a crucial role in restoring functionality.
Advantages of Bone Transport
Natural Lengthening Process
Bone transport mimics the body’s natural bone growth process, resulting in stronger and more natural bone formation.
Preservation of Bone Strength
By preserving the blood supply and minimizing trauma to the bone, bone transport maintains the strength and integrity of the newly formed bone.
Reduced Soft Tissue Complications
The gradual nature of bone transport reduces the risk of soft tissue complications often associated with more rapid lengthening methods.
Customizable to Individual Needs
Bone transport allows for customization based on the patient’s specific needs, making it a versatile option for various conditions.
Candidate Selection
Who is a Suitable Candidate?
Suitable candidates for bone transport are individuals seeking limb lengthening for functional or aesthetic reasons, and those with congenital or acquired limb discrepancies.
Conditions Ideal for Bone Transport
Bone transport is effective for correcting leg length discrepancies, congenital deformities, and segmental bone defects.
Consultation and Evaluation
Candidates undergo thorough evaluation, including medical history, imaging, and physical examination, to determine their eligibility for the procedure.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Postoperative Care
After the fixators are removed, patients require postoperative care and monitoring to ensure proper healing and minimize complications.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Physical therapy is essential to regain strength, mobility, and function. A tailored rehabilitation plan is designed based on the individual’s progress.
Expected Recovery Timeline
The recovery timeline varies based on factors such as the extent of lengthening and the individual’s healing capacity. Most individuals can resume normal activities within several months.
Risks and Considerations
Potential Risks of Bone Transport
Complications can include pin tract infections, nerve injuries, and joint contractures. These risks are minimized through proper surgical technique and postoperative care.
Mitigation and Prevention
Adherence to postoperative care instructions, regular follow-up appointments, and careful monitoring can greatly reduce the risk of complications.
Patient Education and Informed Consent
Patients are educated about potential risks and benefits to make informed decisions and provide consent before undergoing the procedure.
The Future of Limb Lengthening
Advancements in Surgical Techniques
Continuous advancements in surgical techniques and technology are expected to further enhance the safety and effectiveness of bone transport procedures.
Integration of Technology
Incorporation of advanced imaging and computer-assisted navigation will likely refine surgical planning and execution.
Patient-Centric Approaches
The future of limb lengthening will focus on tailoring procedures to individual needs, optimizing outcomes, and prioritizing patient satisfaction.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Is bone transport suitable for all types of limb lengthening? While bone transport is versatile, its suitability depends on individual factors. Consultation with a qualified orthopedic surgeon is essential.
- What is the recovery like after bone transport? Recovery involves a combination of postoperative care, physical therapy, and rehabilitation. Most patients can gradually resume normal activities within a few months.
- Are there age restrictions for bone transport procedures? Age is a consideration, but each case is assessed individually. Pediatric and adult patients may be candidates for bone transport based on their unique circumstances.
- Can bone transport be combined with other procedures? Depending on the patient’s needs, bone transport can be combined with other orthopedic procedures to address multiple issues simultaneously.
- Where can I learn more about bone transport for limb lengthening? For further information and resources, visit Cayra Clinic.
Conclusion
Bone transport for limb lengthening represents a significant advancement in orthopedic surgery, offering a holistic approach to achieving balanced proportions and functional improvement. By embracing innovative techniques like bone transport, individuals can confidently embark on a journey toward enhanced quality of life and a brighter future.